National Bureau of Economic Research
Latest from the NBER
2025, 17th Annual Feldstein Lecture, N. Gregory Mankiw," The Fiscal Future"
video
N. Gregory Mankiw, Robert M. Beren Professor of Economics at Harvard University, presented the 2025 Martin Feldstein Lecture on "The Fiscal Future," examining the trajectory of US government debt—which is projected to reach 156 percent of GDP by 2055. He analyzed five possible outcomes to address this fiscal path: extraordinary economic growth, government default, large-scale money creation, substantial spending cuts, and large tax increases, concluding that significant tax increases, potentially including a value-added tax, represent the most likely solution. The Feldstein Lecture Series was launched in 2009 to celebrate the late Martin Feldstein's three decades of transformative leadership of the NBER.
A research summary from the monthly NBER Digest
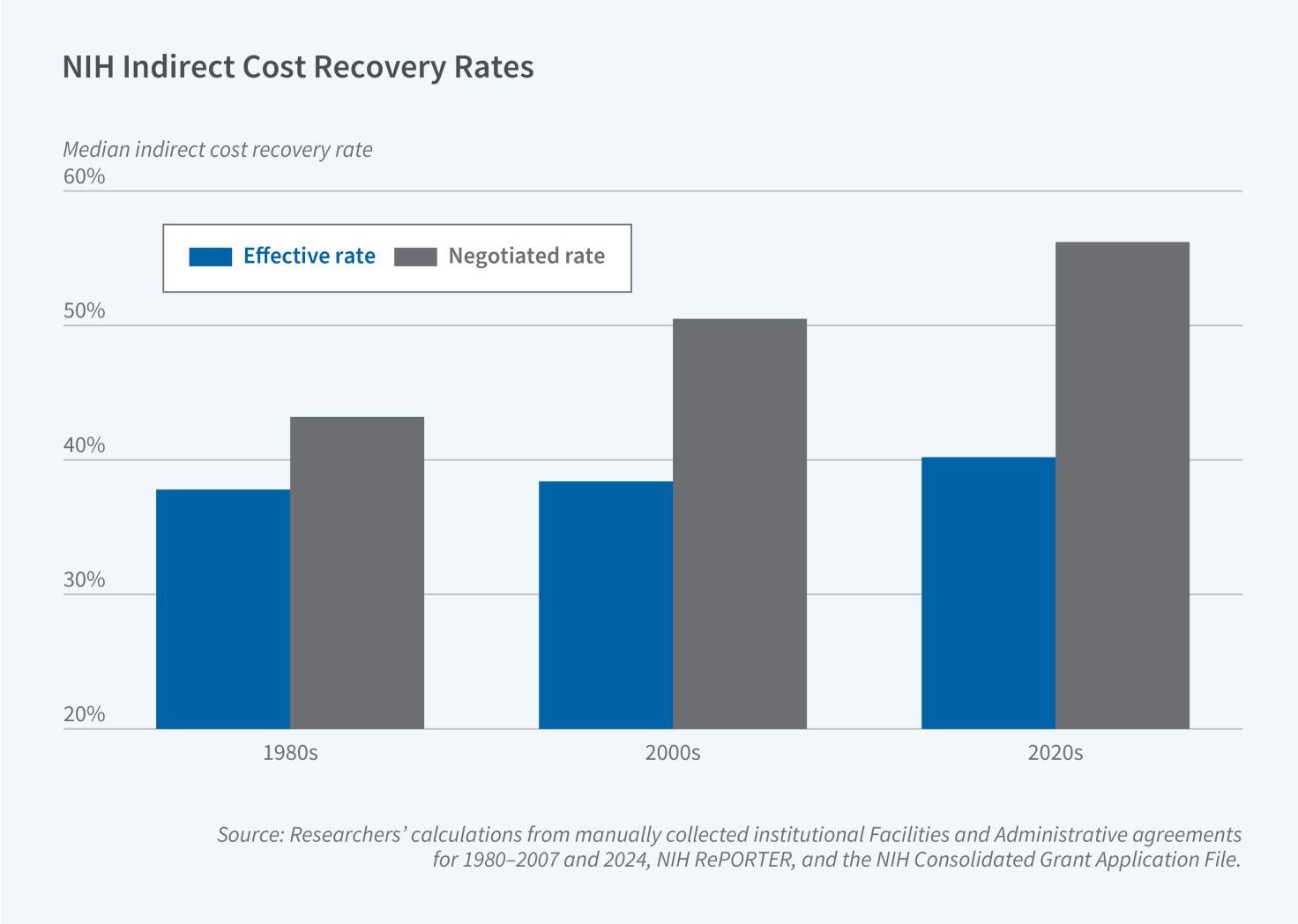
Indirect Cost Recovery in Research Funding
article
For more than 75 years, the federal government has been the largest funder of scientific research at US colleges and universities. Federal science funding includes both direct costs for specific research activities and indirect costs that support the facilities, equipment, and administrative expenses that are needed to conduct these activities.
Federal reimbursement for facilities and administrative (F&A) expenses was introduced during World War II as a way of compensating universities, hospitals, and companies conducting war-related research for expenses associated with lab space, shared instruments...
From the NBER Bulletin on Health
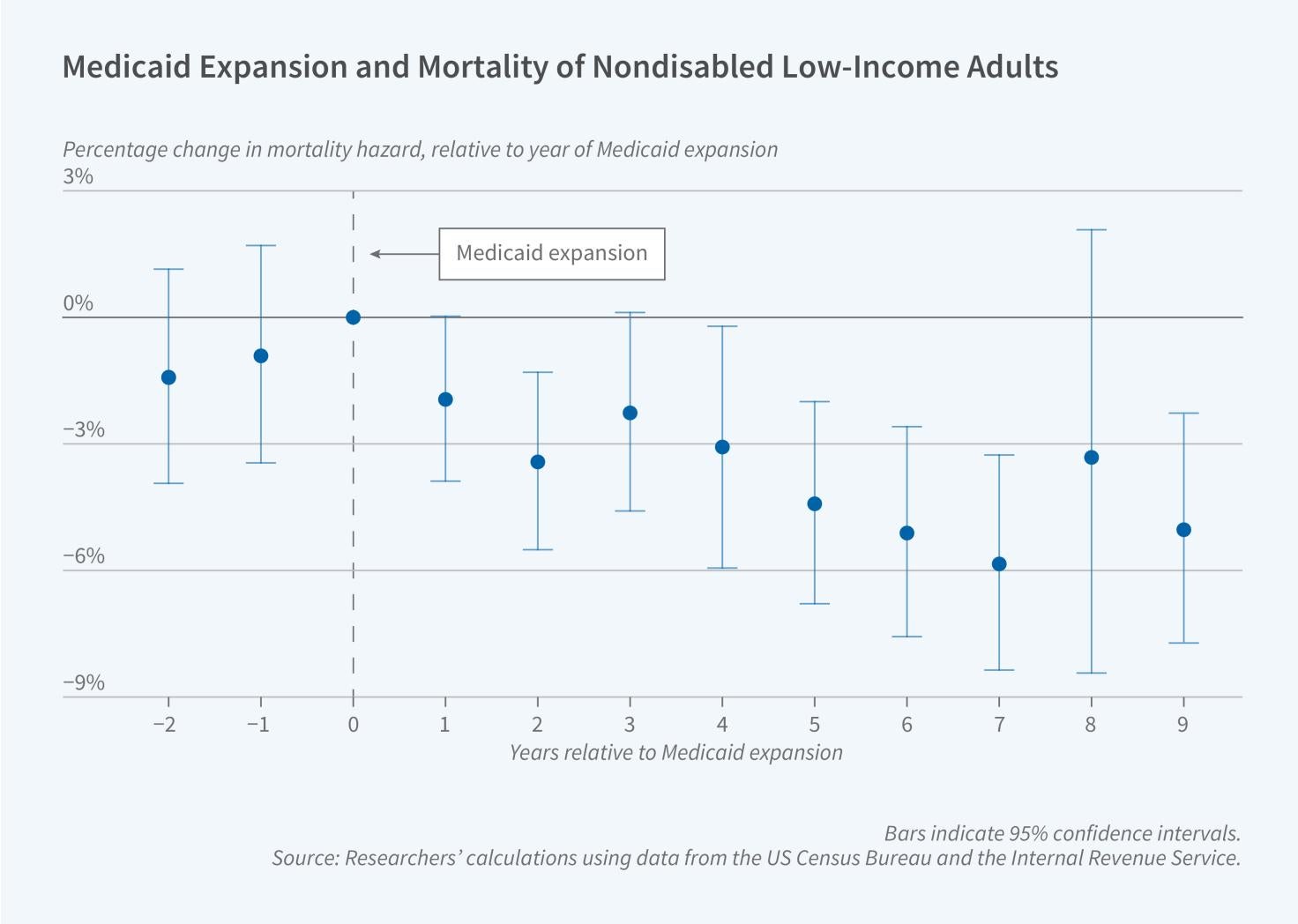
Medicaid’s Lifesaving Effects on Low-Income Adults
article
Lower-income adults in the US are more likely to lack health insurance and to suffer worse health, a correlation that raises the long-standing question of whether health insurance affects health. In Saved by Medicaid: New Evidence on Health Insurance and Mortality from the Universe of Low-Income Adults (NBER Working Paper 33719), Angela Wyse and Bruce D. Meyer present new evidence on this question by evaluating the consequences of recent Medicaid expansions.
To study the impact of Medicaid on mortality, the researchers exploit variation in the state-level adoption and timing of expansions of Medicaid eligibility to childless, nondisabled, non-elderly adults. Most, but…
From the NBER Reporter: Research, program, and conference summaries
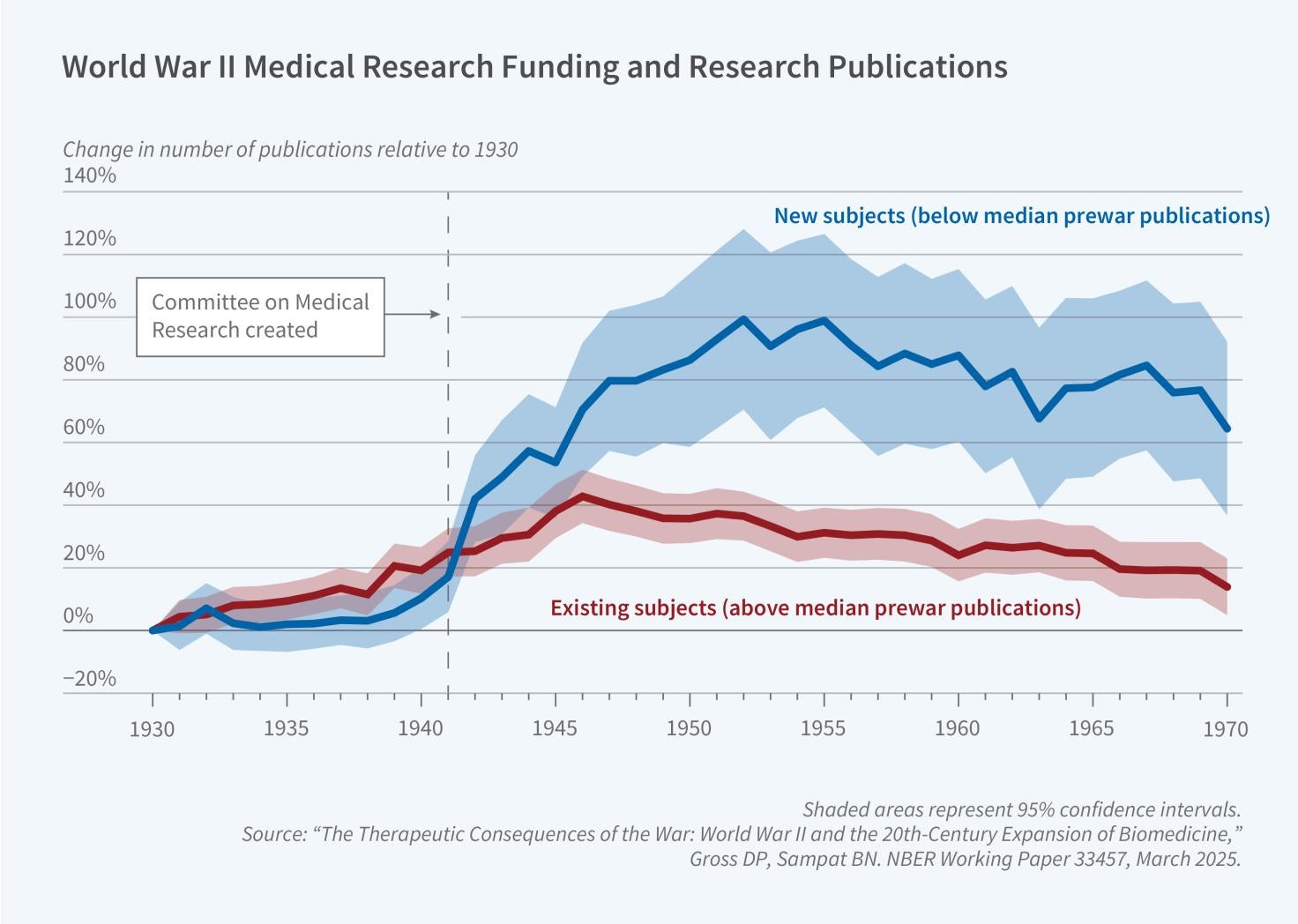
Program Report: Development of the American Economy
article
The Development of the American Economy (DAE) program was one of the first research programs launched by Martin Feldstein in 1978 when he formalized the modern structure of the NBER.
The mission of the program is to research historical aspects of the American economy. Its members are economic historians whose specific interests span many subfields within economics, including macroeconomics, labor economics, finance, political economy, trade, and industrial organization. Broadly, economic history research comes in two flavors. First, economic historians study the evolution of economic trends that illuminate issues relevant to the modern economy, such as the entry of women in the labor force and the moderation of economic crises over time. Second, economic historians use the natural experiments offered by history to test economic…
From the NBER Bulletin on Entrepreneurship
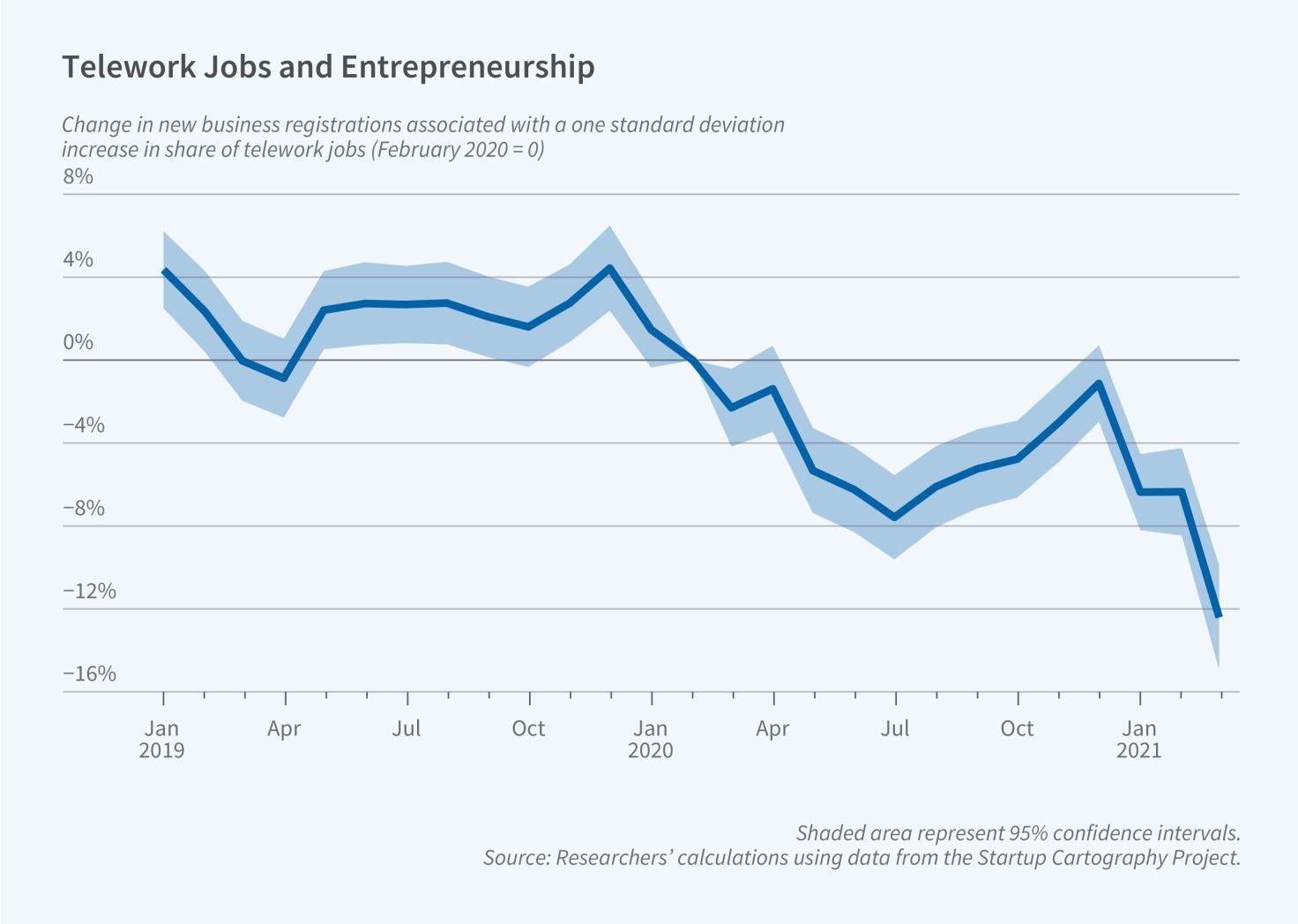
Entrepreneurship as an Alternative to Flexibility at Work
article
The surge in remote work in recent years has transformed labor markets, with potentially important implications for the interaction between workplace flexibility and entrepreneurship. In Hustling from Home? Work from Home Flexibility and Entrepreneurial Entry (NBER Working Paper 33237), John M. Barrios, Yael Hochberg, and Hanyi (Livia) Yi explore whether the increased flexibility provided by work-from-home (WFH) arrangements has affected entrepreneurial decisions. They focus on the COVID-19 pandemic as a natural experiment and analyze how the sudden shift to remote work affected new business creation. Guided…
Featured Working Papers
Independent nursing facilities acquired by nursing-home chains over the period 1999–2019 received, on average, 5 percent fewer health deficiency citations in the two years following acquisition than comparable nursing homes that remained independent, Pinka Chatterji, Chun-Yu Ho, and Wenqing Li find.
Children raised in net worth poverty (NWP), defined as living in households with wealth less than one quarter of the federal poverty line, were less likely to graduate from high school, and even less likely to attend college, than their counterparts in higher net worth households, according to Christina M. Gibson-Davis, Lisa A. Keister, Lisa A. Gennetian, and Shuyi Qiu.
The City University of New York’s 2015 Accelerate, Complete, and Engage program generates $3.06 of net social benefits per taxpayer dollar invested, or $8.30 per dollar when second-generation benefits are considered, according to new research by Judith Scott-Clayton, Irwin Garfinkel, Elizabeth Ananat, Sophie M. Collyer, Robert Paul Hartley, Anastasia Koutavas, Buyi Wang, and Christopher Wimer.
In 13 northern European countries—Belgium, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Iceland, Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, and the UK—the historical u-shape in life satisfaction by age has been replaced by satisfaction rising with age, according to David G. Blanchflower and Alex Bryson.
Variation in government support for STEM PhD training across agencies and over time since 1950 suggests that when the federal government increases the number of PhD trainees it supports, the number of PhDs awarded rises by approximately the same number, according to Dror Shvadron, Hansen Zhang, Lee Fleming, and Daniel P. Gross.
In the News
Recent citations of NBER research in the media
_______________________________________
Research Projects
Conferences
Books & Chapters
Through a partnership with the University of Chicago Press, the NBER publishes the proceedings of four annual conferences as well as other research studies associated with NBER-based research projects.
Videos
Recordings of presentations, keynote addresses, and panel discussions at NBER conferences are available on the Videos page.